In order to clarify doubts about the fixed internet technology used by telecommunications operators, we will address in this article the main differences between ADSL, HFC and fiber technology.
What is ADSL?
There are several ways to access the internet and one of the first that emerged was the Assymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL). This standard is still very popular in Spain today because it is cheaper to implement due to the use of the existing telephone line for internet data transmission. In addition, its cabling is cheaper than other technologies such as HFC and fiber, which will be explained later.
There are variations of this DLS technology, they are: ADSL2, ADSL2+, VDSL, VDSL2 and VDSL2 Phantom
ADSL appeared in 1999 and has a download capacity of up to 8Mb/s (megabits per second). Its upload can reach a speed of up to 1Mb/s, but later a simplified version of the technology called ADSL Lite appeared that has a download capacity of up to 1,5Mb/s and 512Kb/s of upload.
The internet connection via ADSL is made through a cable that has a pair of metallic wires. This type of connection ends up limiting its ability to transmit over long distances between the user's modem and the DSLAM (Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer). The DSLAM is the "closet" that has several ports to distribute the internet signal to homes or buildings. It is important to point out that the DSLAM will not divide the access speed between the lines, that is, if your neighbor is using the speed at its maximum available, it will not affect the quality of your internet.
The maximum distance supported by the technology is up to 6 km, depending on the quality of the equipment used at the ends. However, the ideal is not to exceed 4 km. It is because of this that in rural areas, people choose to use the internet via radio.
The higher the internet speed, the shorter the distance between the user's modem and the DSLAM will have to be. For example:
If we use long-range VDSL2, we can have a distance between 1,2Km and 1,5Km to have access to a download speed of up to 30Mb/s. If we use short-range VDSL2, it will be possible to reach a speed of up to 100Mb/s, but at a distance of 350 meters from the DSLAM.
What is HFC?
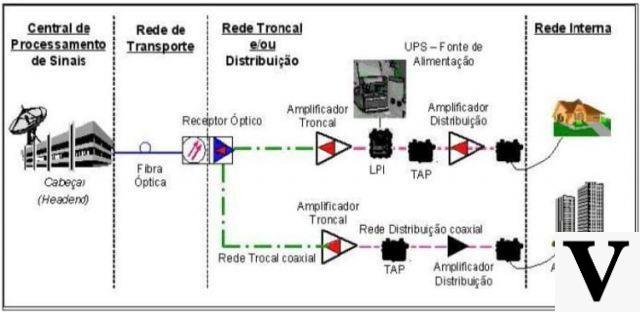
Hybrid Fiber Coax (HFC) technology consists of the use of fiber optic cables and coaxial cables. The fiber optic cables leave the central, pass through the poles until they get closer to homes and buildings and connect to an optical receiver. Then, coaxial cables will come out of the receiver that will distribute the signal to the houses, passing through trunk amplifiers, distribution amplifiers and finally the TAPs that will distribute cables to the houses or buildings.
Coaxial cables have less interference than metallic-pair cables (ADSL) because they have twisted copper pairs and a different symmetry, causing the electromagnetic field to be confined between the inner wire and the outer mesh. This makes coaxial cable able to reach much greater distances than telephone cables and at the same time reach higher transmission speeds (download and upload).
However, despite having a superior performance to the metallic pair cable of the ADSL internet, its geometry still has imperfections, causing small radiations of energy where the signal travels. This makes it somewhat susceptible to interference. This interference ends up affecting the upload capacity and ping of the internet.
The HFC suffers performance and speed drops due to the way the optical node (NODE) is used. When the optical fiber reaches it to convert the optical signal to electrical and later reach the customer, there is the division of coaxial cables, which ideally should be placed a certain number of ports.
Care with the number of ports available on each NODE is necessary so that there is no drop in the quality of the signal distribution. This is usually calculated according to the consumption profile of customers in a given region, but what happens is that most of the time the telecommunications company, in order to save and earn more, uses the same NODE for a large number of customers. The result of this is that at peak times of internet usage by users there will be a big drop in performance and speed.
- How to download videos from almost ANY website without programs in 2022?
- Top 10 YouTube channels
What is fiber?
The fiber optic cable comes to solve several barriers that the technologies mentioned above have, such as distance to transmit lossless speed, interference caused by electromagnetism and, finally, at high speed.
However, in order to achieve high speed, certain care must be taken, as fiber optic cables are fragile and do not support curves with very sharp angles, which impair the passage of the signal. Because of this, it is important to have a specialized team to install the fiber in homes and buildings to deliver a quality signal, without attenuation.
Despite having a high cost for deployment, the durability of optical fiber is considerably greater than that of copper cables and there is very little signal loss due to its immunity against electromagnetic interference, allowing it to be able to carry a signal with strong peak intensity. the tip.
The technology most used for the installation of optical fibers by operators is the Gigabit Passive Optical Network (G-PON) which is capable of transmitting the signal for more than 60 km and delivering the download signal with 94% efficiency and upload with 93% of efficiency, that is, the loss of signal is almost nil. GPON is capable of reaching speeds of up to 2,5Gbits for download and 1,2Gbits for upload.
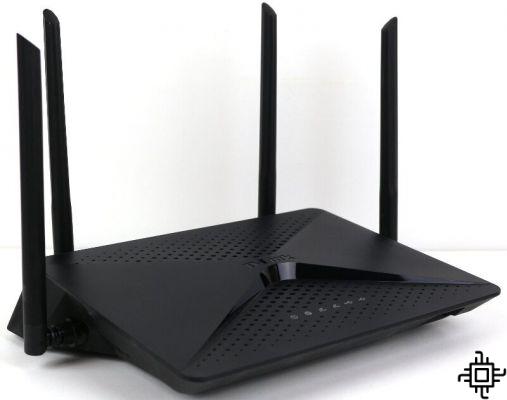
What can I do to get the most out of my internet speed?
To ensure a speed equal to or at least close to the contracted plan, without oscillations or drops, the first rule is not to use the modem/router offered by your operator to transmit the internet via Wi-Fi (by cable is ok). It is necessary to take this attitude because of the poor quality equipment they offer and for that the consumer has to bear the costs to have a quality internet at their disposal.
The first thing to do is to have a grounding socket available and a DSP (surge protection device) with a built-in line filter, such as those from the manufacturer Clamper.
Next, one should look for a router that has gigabit ports and dual band signal transmission (2.4Ghz and 5.0Ghz). It is important that the router is dual band because of the low transmission capacity of the 2.4Ghz band which limits the transmission speed generally to 100Mb/s for less, while the 5Ghz band is able to overcome, for example, the barrier of 200Mb/s quietly.
Finally, it is recommended for those who use streaming videos and play online to use CAT6 type network cables to connect the operator's modem to the Wi-Fi router or to the computer.
Note: Avoid wifi signal repeaters, use only Access Point (AP) or wifi routers. This will keep the signal strong and with quality.