Asian countries and the United States are always at the forefront when it comes to technology and digital innovation. In particular, the internet in these countries is the most prominent point in terms of revolution in the world of communications, way of life, technologies in general and now, including production systems. We are talking about the internet generations, 2G, 3G, 4G and the topic in question: 5G.
Currently, the 4G network is already present in several places around the world, even so, 3G is still dominant. Faced with this, companies are already working hard for the deployment of the 5G network. In the United States, the 6G network is already being talked about and treated as an important issue. But for now, the focus is still on the 5G network that has already arrived in some places.
What is 5G?
5G is the next (fifth) generation of mobile internet connectivity that promises much faster data download and upload speeds, wider coverage and more stable connections. It's about making better use of the radio wave spectrum and allowing many more devices to access the mobile internet at the same time.
In summary, 5G is the new generation of internet for cell phones and mobile devices, which will bring much higher speeds than the current 4G, in addition to less intermittence, more stability and the possibility of more devices connected at the same time.
What is 5G for?
Each network has a different preparation and design, 2G was designed for voice digitization, 3G for mobile internet data and 4G to support even more the large flow of data such as streaming music and video, while the 5G should, in addition to downloads of up to 20 Gb/s, be able to serve trillions of connected devices, not just people, but home appliances, drones and robots. Everything will be able to communicate, thanks to 5G.
To complete, the 5G network, in addition to offering faster connections in general, is also aimed at the internet of things. In an increasingly connected world, the trend is that more and more devices can be connected and, of course, at more affordable prices.
Home appliances and other common appliances, including those connected to the internet, will become more efficient, providing benefits in the areas of entertainment, agriculture, industry, health, energy and virtual reality.
The 5G network will also allow more devices to be connected at the same time, multiplying the number of possible devices by 100.
With regard to the environment, the expectation is that there will be a 90% reduction in energy consumption.
What is the speed of the 5G internet?
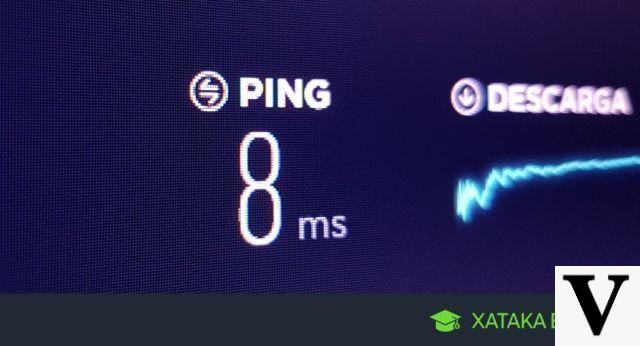
In terms of speed for the consumer, it might be a little less than the full capacity that 5G can achieve. Like the 4G LTE network, which can reach a transfer speed of 1 gigabit per second, but the user doesn't have that access. With the fifth generation it works in the same way, however, from 20 Gb/s the consumer can get something above 10Gbps, but this fact cannot yet be confirmed.
The speed of the fifth generation has a difference of up to 250 times faster than the fourth, which means that considerable changes are coming to the way things work.
One of the main improvements that 5G incorporates is the reduction of latency, that is, the response time that a cell phone takes between receiving the signal and executing it. Therefore, the lower the latency, the faster the device responds when triggered from a distance.
As a comparison, 4G has a delay of 10 milliseconds, while 5G is reduced to 1 millisecond. However, there are obstacles such as walls, buildings, signals and waves that can reduce or affect the quality of speed.
A demo of 5G speeds:
band and frequency
There is a path through which smartphone data travels to generate communication. This path is called bandwidth, and it is responsible for managing data transfer. For this to happen, voice, video, audio or text information is converted from a telephone into an electrical signal that passes to a cell tower via radio. After that, it passes from the tower over a network that takes the information to a server or another phone. This data transfer promises to have a much wider and higher frequency band in 5G.
As a result of the bandwidth increase, the frequency also expands. This raises the number of devices that will stay connected on 5G and other mobile networks.
4G frequency bands are up to 20 MHz, and 5G, even though it does not have a defined standard, should be around 60 GHz. The number is higher because it is a new generation of mobile network, which is not yet widely used, and precisely because of this, it can receive data more freely. In short, the higher frequency bands promise more space for data transition and thus, it is more difficult to be affected by interference or obstacles that alter the speed.
There are several applications that the fifth generation mobile network can bring, leading to greater infrastructure for virtual reality, high-precision agriculture and even cloud computing, for example. To get to 5G, mobile operators will work on network virtualization and better investment in 4G, as it will support 5G.
What are the risks of 5G for our health?Cars, appliances, devices that can be wearable like glasses, all of them can be connected to the 5G network and talk to each other.
Smartphones compatible with the 5G network
Taking into account the advances of the 5G network, several companies have already launched devices compatible with the technology. The first and main companies to launch devices equipped with the fifth generation of internet are Huawei, LG, Samsung, Xiaomi and ZTE.
Check the list of devices compatible with the 5G network:
- Samsung Galaxy S10 5G: The device is an upgrade of the standard S10, however, with compatibility with the 5G network.
- Huawei Mate X: Huawei presented the device during this year's MWC and it arrives with a 6,6-inch screen and 11 mm thickness when folded (the device is foldable). The processor is Kirin 980, it also has 8 GB of RAM, 512 GB of storage and Balong 5000 multi-mode 5G chipset and 4.500 mAh battery. It will initially be released in Europe.
- LG V50 ThinQ: The model arrives with Snapdragon 855 processor, 6,4-inch QHD + OLED display. The device was unveiled during MWC 2019.
- Xiaomi Mi Mix 3 5G: The device has a 6,39-inch OLED display with an infinity screen design. The model has 6 GB of RAM and up to 128 GB of storage.
The internet of things
The next big step for the market to make 5G viable is to offer an "internet of things" (IoT) service. This could be possible thanks to the reduction of latency, which improves the internet of things to the point that we will have everything connected, in addition to just devices. Cars, appliances, devices that can be wearable like glasses, all of them can be connected to the 5G network and talk to each other.
According to Huawei, there are currently seven billion devices connected to the internet, while the forecast for 2025 with widespread IoT is 100 billion connected devices. And the high point is that these products will not necessarily need to be connected by wi-fi, as they will be able to use 5G if there is a connection drop.
Self-driving cars have a fundamental need for the fifth-generation internet to function safely, as vehicles will need to process several terabytes of data a day. In this situation, the car must have sensors such as cameras, systems and radars to capture information from the street, such as signs and pedestrians, and thus must process it to react in milliseconds. Watch a video from Huawei about the new technology:
In this context, low latency comes into play, as the reaction of commands for driverless cars must be as fast and correct as possible. In addition, the network should still be covering in-vehicle entertainment features such as streaming music or news.
And they still have many things that will improve their capabilities, such as telepresence robots that allow videoconferencing with people from far away, with an image and stable connection. Personal assistants for the home are also part of it, who can benefit from the constant connection. Cloud storage, music and video streaming services, virtual reality can all benefit from 5G, making the experience much more immersive.

Challenges to apply 5G
Currently, it is not enough for technology to be built to work. There are physical limitations, especially in continental countries such as Spain. For the operation of 5G networks, investments in network infrastructure would be necessary, as was the migration from 3G to 4G.
In addition to the physical infrastructure, antennas, equipment at access points, it will be necessary to discuss the network spectrum, which is regulated by government agencies. As 4G networks have already saturated the frequencies that could be used by 5G, new, higher frequencies will be needed. These do not cover a region as large as the smaller ones, to compensate, operators will have to install more transmission bases.
How is the 5G network scenario in the world
In several parts of the world, the 5G network is already in full development, and in Asian countries and the United States they are much further along in this technological race.
In the United States, for example, operators such as AT&T and Verizon have already started testing the network. In China, commercial launch is expected in 2020, through China Unicom and China Telecom.
Japan is expected to launch 5G ahead of the Summer Olympics and Paralympics in August 2020.
According to a document from the European Observatory, in addition to the United States, China, Japan and the European Union, other countries such as India, Australia, Canada, South Africa and the Gulf countries, such as the United Arab Emirates, Qatar and Saudi Arabia are at the forefront of 5G network development.
And in Spain?
Spain is taking slow steps in relation to the deployment of the 5G network. According to the president of Anatel (National Telecommunications Agency), Leonardo Euler, said that a public notice for 5G should be launched later this year and that an auction will take place until March 2020. The process is fundamental for the installation of the mobile internet, as it establishes who has the right to exploit the spectrum.
Even so, the arrival of the 5G network in the country is not yet planned for next year. The expectation is that commercial plans with the 5G network will be released from 2021.