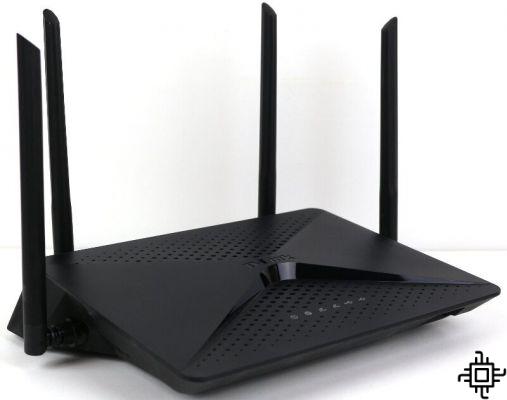
If you are considering replacing or upgrading your old router, you may come across terms like "dual band" and even "triple band", which refers to a Wi-Fi router that uses two frequency bands (2.4Ghz to 5Ghz) or three (2.4GHz, 5GHz or 6GHz). After all, what do these numbers mean? Know what the differences are and which one you should use.
What is the difference between 2.4Ghz, 5Ghz and 6Ghz WiFi?
While it may seem confusing, these numbers refer to three different radio wavelengths (often called "bands" or "frequencies"). Currently, the most used Wi-fi network standard in Spain is Wi-fi 5, identified by the letters "AC" (802.11ac Wi-fi standard), which uses two bands (2.4Ghz to 5Ghz) and is therefore called "Dual Band" or "Dual Band". However, Wi-fi 6, identified by the letters "AX" (Wi-fi 802.11ax standard) on routers, has brought interesting technologies that can help in the performance of tasks that depend on internet performance.
Wi-fi 6 has two variants, Wi-fi 6 and Wi-fi 6E, where the latter is an improved version of the standard and has the great advantage of using the 6Ghz band. However, this frequency, although it can provide considerably higher speeds compared to the 5Ghz band, it has a smaller signal range capability.
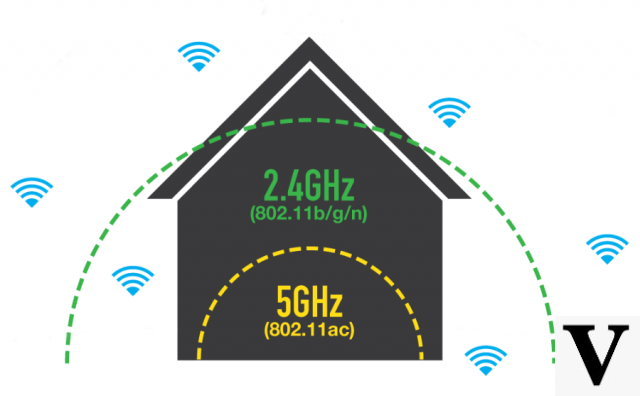
A 2.4Ghz wireless transmission provides internet for a larger area but sacrifices speed, while 5Ghz and 6Ghz provide faster speeds for a smaller area. In other words, in practice, in terms of coverage area capacity, we have the following order of frequency bands, going from the one with the greatest range to the one with the worst transmission capacity by distance: 2,4Ghz > 5Ghz > 6Ghz.
Each router is designed to provide a certain set of frequencies, and you should consider which WiFi band and channel will best suit your needs and provide optimal performance.
Final report: Do not confuse 5Ghz with 5G, they are different things and we explain in this article.
Listed below are the different WiFi standards that are most common today, their frequencies, distances and theoretical speeds. Keep in mind that the speeds you get with your router will vary based on the company offering the internet service, the internet data transmission technology (learn more about here) and the technology used by the Wi-Fi device and device. client (mobile, notebook, tablet, desktop, etc.).
Range Comparison - 2.4 GHz vs. 5Ghz
| Standard | Frequency | theoretical distance | real world distance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 802.11a | 5Ghz | 119 meters | 60 meters |
| 802.11b | 2.4Ghz | 140 meters | 70 meters |
| 802.11g | 2.4Ghz | 11 meters | 19 meters |
| 802.11n | 2.4Ghz | 250 meters | 125 meters |
| 802.11n | 5Ghz | 140 meters | 70 meters |
| 802.11ac | 5Ghz | up to 250 meters (amplified) | up to 125 meters (amplified) |
Speed Comparison - 2.4Ghz vs. 5Ghz
| Standard | Frequency | theoretical speed | real world speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| 802.11a | 5Ghz | 6-54 Mbps | 3-32 Mbps |
| 802.11b | 2.4Ghz | 11 Mbps | 2-3 Mbps |
| 802.11g | 2.4Ghz | 54 Mbps | 10 -29 Mbps |
| 802.11n | 2.4Ghz | 300 Mpbs | 150 Mbps |
| 802.11n | 5Ghz | 900 Mbps | 450Mbps |
| 802.11ac | 5Ghz | 433 Mbps - 1,7 Gbps | 210 Mbps - 1 G |
What are dual and tri-band routers?
Most modern routers act as dual or tri-band routers. A dual-band router is one that transmits both a 2.4Ghz and 5Ghz signal from the same unit, giving you two Wi-Fi networks and the best of both worlds. Dual band routers can be:
- Dual band selectable: A selectable dual-band router offers both 2.4Ghz and 5Ghz WiFi network, but you can only use one at a time. You actually need to use a switch to tell what band you want to use.
- simultaneous dual band: A dual-brand router simultaneously broadcasts separate 2.4Ghz and 5Ghz WiFi networks at the same time, giving you two WiFi networks that you can choose from when setting up a device. Some router brands also allow you to assign the same SSID to both bands so that devices only see a single network - although both are still operational. They tend to be a little more expensive than selectable dual-band routers, but the advantages of having both bands operating simultaneously often outweigh the difference in cost.
Capability present only in Wi-fi 6E, a tri-band router operates three bands simultaneously, 2,4Ghz, 5Ghz (Wifi 5 and Wifi 6) and 6Ghz. When using the 6Ghz band, the user will be able to obtain a higher transmission speed than the Wi-fi 6 and Wi-fi 5 standards. With the Wi-fi 6E, it will be possible to obtain 600Mbps through a channel of 80Mhz and 1200Mbps a 160Mhz channel. To better understand what this means and why to get this result, we have to understand what channels are.
What are frequency band channels?
To transmit the Wi-Fi signal, channels are used, measured in Megahertz (Mhz). If a Wi-fi band (5Ghz, 2,4Ghz or 6Ghz) is a highway, the channels are the lanes. In Spain, ANATEL allows the use of 13 20Mhz channels each in the 2,4Ghz Wi-Fi band, while 5 channels are allowed in the 24Ghz band, where instead of using 20MHz as the 2,4Ghz and some 5Ghz channels (which only accept this band), frequencies of 40Mhz, 80MHz and up to 160Mhz are used.
Know that the wider the track, the more speed you can get from it. This is a great advantage of the 6GHz band, where the number of 160Mhz channels (the highest range currently) available is seven against only 2 in the same range at 5Ghz.
To obtain a wider range (channel), the set of two channels is generally used. Examples:
- 40Mhz channel - made up of two 20Mhz channels.
- 80Mhz channel - made up of two 40Mhz channels.
- 160Mhz channel - made up of two 80Mhz channels.
To avoid interference, the ideal is to do a spectrum scan on the spot to know which 2,4Ghz, 5Ghz or 6Ghz channels are being occupied (or with fewer routers using). For this, programs such as Vistumbler (software for computers with Wi-fi antenna) and the WiFiman app (iOS and Android) are used.
Recommended articles for reading:
- What are the 2,4GHz and 5GHz frequency band channels? Which one is the best?
- What is the difference between Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E routers? Do you need them?
Which frequency should you choose - 2.4Ghz, 5Ghz or 6Ghz?
While you may not have many of these devices in your home, if you live in an apartment surrounded by other people, chances are that this 2.4Ghz band is congested with multiple devices.
If you have a device that doesn't move and is close to your router (but you can't connect it with an Ethernet cable), we recommend setting it to 5Ghz or 6Ghz frequencies, to reduce congestion and take advantage of the higher speeds that 5Ghz and 6Ghz band can provide.
On the other hand, if you have a device that moves around a lot in your house (like your smartphone), and is usually farther away from your router, we recommend that you set that device to the 2.4Ghz frequency. This wavelength has a longer range and can penetrate solid objects more easily than the 5Ghz and 6GHz bands, making it ideal for devices that move or are located further away from the router.
2.4Ghz Summary
- Cons: lower data rate; more prone to interference; generally more devices using that frequency.
- Pros: Larger coverage area; better at penetrating solid objects.
- Maximum connection speed: ~ 150 Mbps.
- Maximum signal range (from the router): ~410 feet.
5Ghz Summary
- Pros: Higher data rate; less prone to interference; generally fewer devices using this frequency.
- Cons: Smaller coverage area; less successful in penetrating solid objects.
- Maximum connection speed: ~ 1 Gbps.
- Maximum signal range (from the router): ~410 feet amplified.
If you choose 2.4Ghz, 5Ghz and 6Ghz, you need to check if your modem/router/Access Point (AP) and client device (smartphone, tablet, notebook, desktop) are supported to use the same frequency. Check your specific router model for compatibility and frequency specifications.
Also see what WiFi 6 is and its benefits:
What is the difference between Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E routers? Do you need them?